Abstract
BACKGROUND
Treatment (Tx) options in RRMM are limited by RI, a comorbidity present at diagnosis in 20% to 30% of pts with MM, of whom ≈ 2% to 13% require hemodialysis. In addition to being associated with poor prognosis and short survival, RI may also have an impact on the PK of drugs that are primarily excreted by the kidneys. POM administered orally is well absorbed in an approximate dose-proportional manner up to ≈ 10 mg/day, with minimal accumulation (≈ 30%). POM has a half-life of ≈ 8 hours and is primarily eliminated renally (≈ 73% of dose); however, unchanged drug in urine accounts for < 5% of dose, indicating extensive metabolism prior to excretion. The multicenter, phase 2 MM-013 trial investigated the safety, efficacy, and PK of POM + LoDEX in pts with RRMM and moderate or severe RI, including those on hemodialysis.
METHODS
A total of 81 pts with RRMM and RI were enrolled in 3 cohorts: (A) moderate RI (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] ≥ 30 to < 45 mL/min/1.73m2), (B) severe RI (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m2), and (C) severe RI requiring hemodialysis. Pts were eligible if they received ≥ 1 prior Tx including lenalidomide (LEN) and progressed during or after their last anti-MM treatment. POM + LoDEX was administered until progressive disease (PD), unacceptable toxicity, death, withdrawal, or loss to follow-up. Overall response rate (ORR) was the primary endpoint. Secondary endpoints included safety, renal response, time to myeloma response, time to renal response, duration of response, progression-free survival (PFS), time to progression, overall survival (OS), and PK. The effect of RI on POM PK was assessed in all cohorts. Pts underwent sampling predose (−30 to −5 minutes prior to dose); 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 8 hours (± 10 minutes) postdose; and 24 hours (± 3 hours) postdose.
RESULTS
There were 33 pts in cohort A, 34 in cohort B, and 14 in cohort C. This analysis presents data collected until January 28, 2017, when 13 pts (16.0%) were still on Tx. A total of 68 pts (84.0%) discontinued Tx, mostly due to PD (48.1%). Median age was 72 years (range, 52‐86 years); 60.5% of pts were male. Median time from diagnosis was 3.8 years. RI was present in all pts, of whom 86.4% had chronic (> 1 month) and 13.6% had acute (≤ 1 month) renal failure. As expected, pts in cohort C had a lower median eGFR (8.9 mL/min/1.73 m² vs 38.8 and 22.2 mL/min/1.73 m² in cohorts A and B, respectively) and a heavier disease burden as indicated by higher involved serum free light chain (sFLC) levels than pts in cohorts A and B at baseline. Median involved sFLC κ and λ levels were > 7250 mg/L in cohort C and < 2250 mg/L in cohorts A and B. Pts received a median of 4 (range, 1-10) prior anti-MM regimens. All pts had prior LEN Tx, and nearly all had prior bortezomib (97.5%). Median relative dose intensity of POM was 0.95 in cohort A, 0.94 in cohort B, and 0.99 in cohort C. ORR was 39.4%, 32.4%, and 14.3% in cohorts A, B, and C respectively. Median PFS was 5.2 months (median follow-up, 4.6 months). At a median follow-up of 7.8 months, median OS was 9.7 months.
Safety results were similar to those from other POM trials. However, grade 3/4 anemia and thrombocytopenia were more common in cohort C, likely due to severe RI requiring hemodialysis.
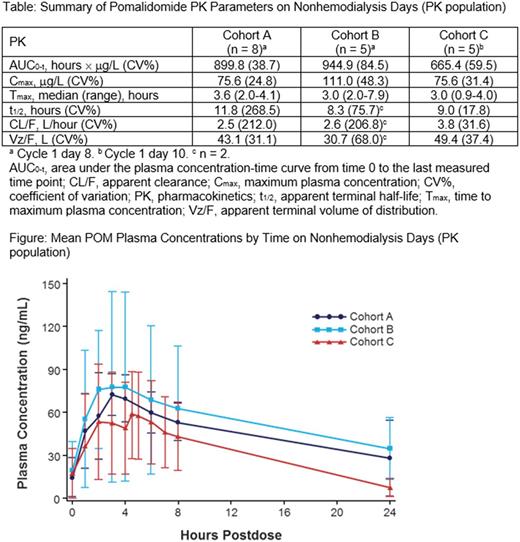
The PK values, including Cmax, plasma exposure, Tmax, mean t½, and CL/F, were similar in the 3 cohorts (Table). The mean POM plasma concentration-time profiles on nonhemodialysis days showed similar trends in all 3 cohorts, with peak concentrations detected at ≈ 4 hours postdose in cohorts A and B and ≈ 1 hour later in cohort C (Figure). In cohort C, during hemodialysis, visual examination of POM concentration-time profiles suggested that the concentrations from the arterial side (withdrawal) were higher than those from the venous side (returning) of the dialyzer.
CONCLUSIONS
POM + LoDEX can be safely administered and is efficacious in pts with RRMM and moderate or severe RI, including those on hemodialysis. Following administration of multiple oral doses of POM 4 mg, the PK of POM was comparable among the 3 renal cohorts. POM dialysis clearances were higher than POM total plasma clearance, suggesting that the hemodialysis procedure significantly removed POM from the blood. Therefore, based on the PK profile, it is recommended that POM be administered after pts undergo hemodialysis.
In addition, dose adjustment is not needed in pts with RRMM and RI because POM clearance and plasma exposure were not affected significantly by RI status.
Sonneveld: Celgene, Amgen, Janssen, Karyopharm, Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene Corporation, Amgen, Janssen, Karyopharm, SkylineDx, PharmaMar: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation, Amgen, Janssen, Karyopharm, PharmaMar, SkylineDx: Honoraria. Weisel: Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Li: Celgene Corporation: Employment. Kueenburg: Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria. Collins: Celgene Corporation: Employment. Di Micco: Celgene Corporation: Employment. Rosettani: Celgene Corporation: Employment. Bacon: Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Dimopoulos: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Genesis Pharma: Research Funding; Amgen Inc, Celgene Corporation, Janssen Biotech Inc, Onyx Pharmaceuticals, an Amgen subsidiary, Takeda Oncology: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Advisory Committee: Amgen Inc, Celgene Corporation, Janssen Biotech Inc, Onyx Pharmaceuticals, an Amgen subsidiary, Takeda Oncology.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal